Our weekly health news roundup gives you an opportunity to catch up on the latest health stories which you may have missed during your busy week. This week the stories focused on Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, thyroid disease and more.
It’s important to keep up with weekly health news to keep you up to date in the ever-changing world of health. And so below are Bel Marra Health’s top health news stories of the week.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may share symptoms but are not the same
Advertisement
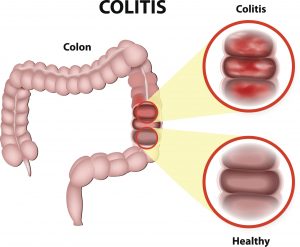 Previous research has found possible overlap of symptoms between IBS and IBD. The researchers found that a common medication to treat ulcerative colitis is effective in the treatment of symptoms related to IBS and a common antidepressant used in IBS may benefit patients with IBD in treating functional symptoms.
Previous research has found possible overlap of symptoms between IBS and IBD. The researchers found that a common medication to treat ulcerative colitis is effective in the treatment of symptoms related to IBS and a common antidepressant used in IBS may benefit patients with IBD in treating functional symptoms.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are common IBDs which affect nearly 1.4 million Americas as of 2012. Both conditions lead to inflammation of the colon and rectum as well as inflammation anywhere from the mouth to the anus – essentially any part of the digestive system. Continue reading…
Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis is a continuum of disorders, can affect location of inflammation in the gut
Genetic data now suggests that Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis is a continuum or progression of disorders influenced by the location of inflammation in the gut.
About 1.4 million Americans have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Diagnosis could be oversimplified though. This according to genetic data that shows the diseases are a complex continuum of disorders influenced by the site of the inflammation involved.
The location of disease in Crohn’s has always been considered important, but there has been a new observation that large bowel Crohn’s disease is halfway between ulcerative colitis and small bowel Crohn’s on the genetic spectrum, which suggests the vital aspects of the disease biology are linked to location. Continue reading…
Thyroid disease can have significant effects on fertility, pregnancy, suggests a new review
Research has found that thyroid disease can have significant implications on fertility and pregnancy and women presenting reproductive health issues should be screened for thyroid problems.
Thyroid hormones help control the metabolism and these same hormones also play a role in growth and development, in particular brain development. Therefore changes in the thyroid can contribute to problems in regards to reproduction prior, during and after conception.
Thyroid disease can either be an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). The recent review of literature explored both thyroid diseases and how they play a role in fertility and pregnancy complications. Continue reading…
Schizophrenia risk may be revealed by face reading, finger length
 Schizophrenia risk may be revealed by face reading and finger length according to research. The findings uncovered that deficits in emotional recognition may be a precursor to schizophrenia symptoms and may help identify those at highest risk to develop the mental disorder.
Schizophrenia risk may be revealed by face reading and finger length according to research. The findings uncovered that deficits in emotional recognition may be a precursor to schizophrenia symptoms and may help identify those at highest risk to develop the mental disorder.
There are criteria set out to help identify those with schizophrenia but nearly 20 to 30 percent of patients who meet the criteria transition into psychosis within three years. The researchers argued that by identifying those at risk earlier through algorithms can receive earlier intervention and prevent serious psychosis. Continue reading…
Systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus) patients are more vulnerable to infections which can lead to mortality
Advertisement
 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients are more vulnerable to infections which can lead to mortality. Researchers found that hospitalizations of lupus patients due to serious infections are on the rise.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients are more vulnerable to infections which can lead to mortality. Researchers found that hospitalizations of lupus patients due to serious infections are on the rise.
SLE, lupus, is an autoimmune disease where the immune system overreacts and attacks healthy joints and organs. Often these patients much take immunosuppressants in order to reduce symptoms but in turn this increases their risk of developing serious infections because their immune system is weak and thus cannot fight off viruses or bacteria. Common infections which SLE patients experience are pneumonia, sepsis, and urinary tract and skin infections.
Serious infections are a serious threat to SLE patients as it increases their risk of mortality and accounts for 13 to 37 percent of hospitalizations and one-third of deaths. Continue reading…


