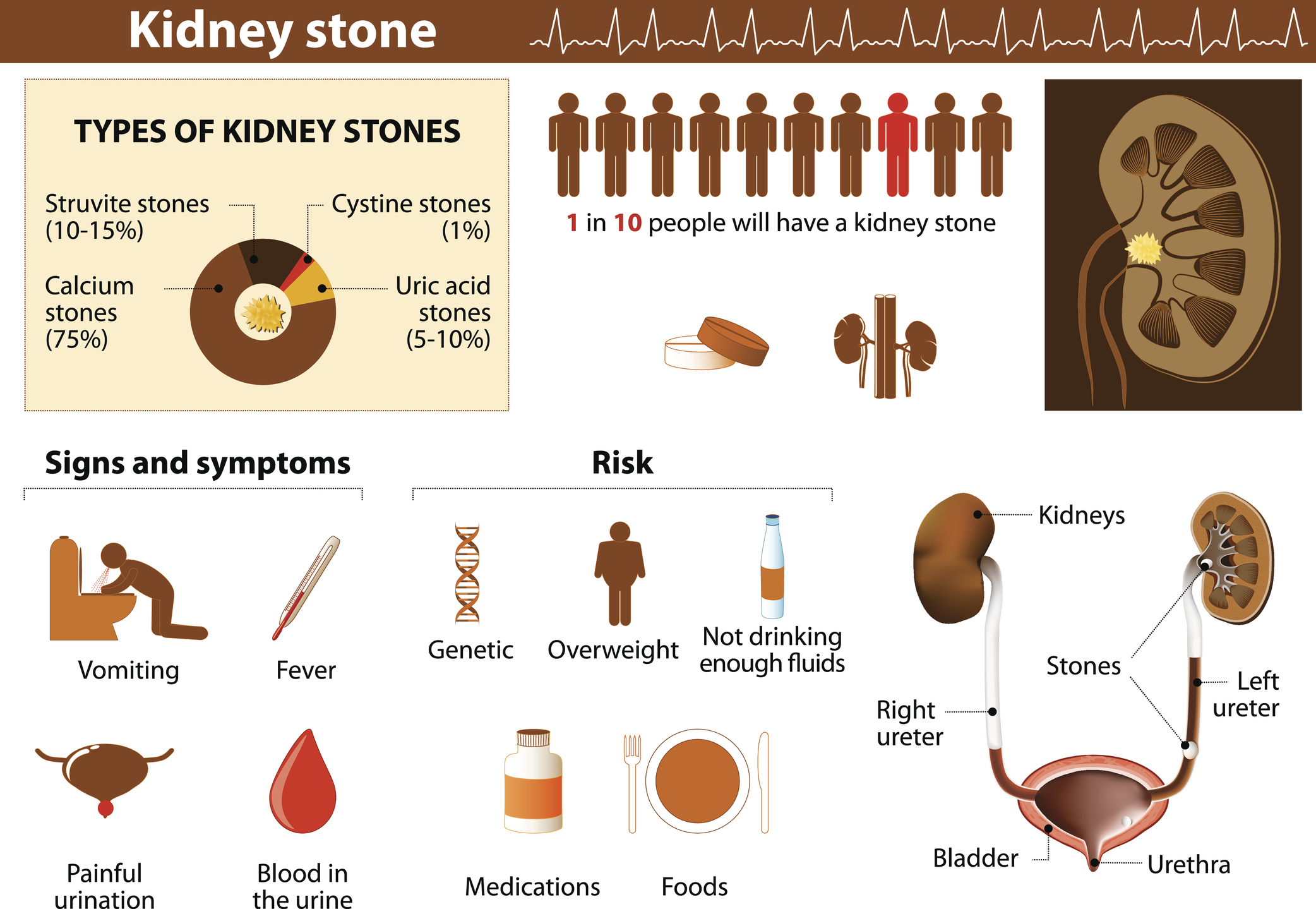
Enlarged prostate treatment may help passage of large kidney stones in the urine
Enlarged prostate treatment may help with the passage of large kidney stones in the urine. The patients in the study were treated with tamsulosin, a common treatment for an enlarged prostate. The researchers found this treatment helped improve kidney stone passage through urine. Researcher Dr. Jeremy Furyk explained, “Kidney stones are a bit of a ...click here to read more