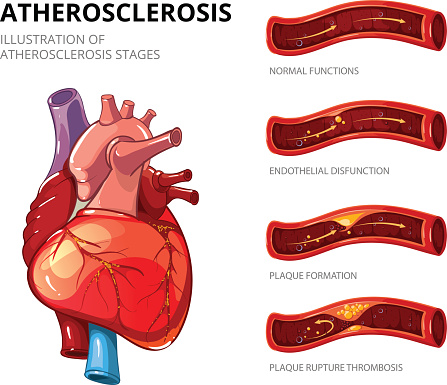
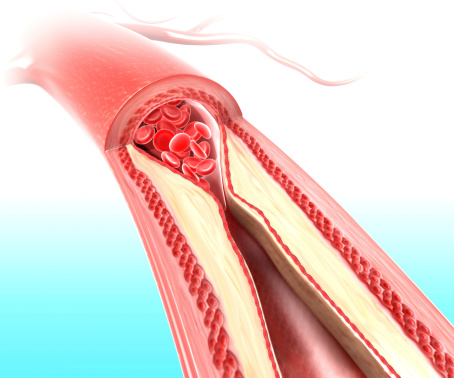
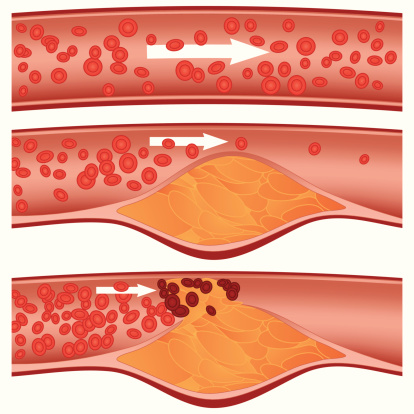
Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis
Systemic sclerosis – scleroderma – is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis, which is hardening of the arteries. The findings come from researchers in Hong Kong who uncovered that scleroderma can contribute to atherosclerosis. Among the known risk factors for atherosclerosis are age and hypertension. Scleroderma is a connective tissue disorder in which the tissue ...click here to read more