 There is a link between influenza and severe sepsis where experts describe the warning signs of sepsis and septic shock in order for you to prevent the complication from occurring to you.
There is a link between influenza and severe sepsis where experts describe the warning signs of sepsis and septic shock in order for you to prevent the complication from occurring to you.
Influenza, or the flu, is caused by a viral infection which mainly affects the respiratory tract and not the digestive system – even though you may have heard the term stomach flu, it isn’t really the flu.
Advertisement
Influenza may progress to a serious condition known as sepsis. Sepsis is the body’s, often deadly, response to an infection or injury and can sometimes be referred to as blood poisoning.
Sepsis, and septic shock, can result from any infection anywhere in the body – including the flu. Worldwide, one-third of those who experience die and those who survive sepsis are often left with chronic conditions or complications like post traumatic stress disorder, chronic fatigue or organ dysfunction.
Experts from the Mayo Clinic have created guidelines to describe warning signs of sepsis and septic shock. Steve Peters, M.D said, “Let’s say one feels some nasal congestion, and achy, like a cold or upper respiratory illness they’d had many times before, or a low-grade temperature of 99 or 100 F, and otherwise they’re up and around and able to drink fluids: That would not call for going to the emergency department. But, if one was not able to take fluids, became more sleepy and lethargic and was lying down all day, and starting to look quite ill or appearing confused, for example — that person should definitely be seen by a doctor.” Dr. Peters suggests the single best thing a person can do with sepsis is maintain fluid levels as the beginning of sepsis causes fluid loss.
Although anyone can develop sepsis those who undergo chemotherapy or take immunosuppressant medications are at highest risk. The elderly and those with open wounds, too, are at high risk for sepsis as well.
Dr. Peters concluded, “Taking your temperature is important, because it gives a good assessment of how severe this might be. Probably the single most important thing is to try to continue taking in fluids. Watch for signs and symptoms, and seek urgent medical care if you suspect sepsis.”
Influenza and severe sepsis, the complex link
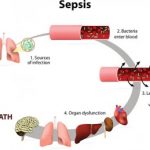 The link between severe sepsis and influenza is quite complex. Severe sepsis is commonly associated with bacterial infections – fungal and parasitic infections, too, can also sometimes cause severe sepsis but are less common. Influenza continues to grow and cause large epidemics thus increasing the rise of sepsis caused by influenza or secondary sepsis by influenza-induced secondary bacterial infection.
The link between severe sepsis and influenza is quite complex. Severe sepsis is commonly associated with bacterial infections – fungal and parasitic infections, too, can also sometimes cause severe sepsis but are less common. Influenza continues to grow and cause large epidemics thus increasing the rise of sepsis caused by influenza or secondary sepsis by influenza-induced secondary bacterial infection.
When an inflammatory response is triggered by influenza it can result in poor outcomes. Like many viruses and infections, influenza interacts with the immune system directly which contributes to severe sepsis or secondary-bacterial sepsis.
There is still much unknown about the link between influenza and severe sepsis, but what is known is that more research needs to be conducted in order to better understand it.
Diagnose sepsis by measuring levels of RNA biomarkers in blood
Researchers have found that measuring RNA in the blood may better help diagnose sepsis. This testing will quickly decipher between sepsis and infection-negative systemic inflammation. The researchers found four RNA transcripts which can be identified to quickly diagnose sepsis.
The researchers conducted analysis on blood samples from 74 patients with sepsis and 31 post-surgical patients with infection-negative inflammation where they identified the four RNA transcripts.
The researchers then went on to validate their findings on five additional cohorts which consisted of 345 patients. Their additional testing was successful in diagnosing sepsis from infection-negative inflammation. Their new classifier – known as SeptiCyte Lab – was not only quicker than traditional testing but was also accurate 90 percent of the time.
The researchers must conduct further testing on larger populations in order to validate their classifier more so. The authors concluded, “In combination with clinical parameters and clinical judgment, SeptiCyte Lab may provide physicians with enhanced confidence in therapeutic decision-making for patients with systemic inflammation.”
Related Reading:
Sepsis, septic shock-related muscle damage repairable by stem cell therapy: Study
Sepsis and septic shock-related muscle damage may be repairable by stem cell therapy, according to new findings. Sepsis is an inflammatory response to a severe infection and affects nearly 28 million people worldwide, claiming the lives of eight million. In those who survive sepsis, life-long complications may occur, which are not only debilitating, but can affect a person’s day to day life. Continue reading…
Seasonal influenza vaccine FDA approved
Advertisement
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a seasonal influenza vaccine containing adjuvant called Fluad. The new vaccine contains three influenza strains and is intended to prevent influenza in those over the age of 65. Fluad is egg-based and contains adjuvant MF59. Adjuvants are added to vaccines to enhance or direct immune response in the vaccinated individual. Continue reading…
Sources:
http://www.sepsis.org/sepsis_and/influenza/
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2015-01/mc-ias011315.php
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4161/viru.27103
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2015-12/p-rma120715.php
